

And finally the outlooks of the work were modeled with AUTOCAD.ĭividing property was investigated in scored tablets compressed by direct compression method.

The performance of the mixing process was also simulated using MATLAB/Simulink, the responses of the mixer speed were determined having 0.175seconds, 0.33 and 0.3902seconds rise time, overshoot and settling time respectively.
SUPERTAB 24AN SOFTWARE
The whole system were PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) controlled and programmed in Siemens SIMANTICS step7 300 software with WINCC HMI operator-panel that enables parameter adjustments and results monitoring in real-time. STEP7 in-built PID controller block (FB41 CONT_C) is used for achieving this task. F_CV ≤ 4.00%) which will terminate Multipoint NIRS analysis and activate for output of processed feed. the CV) of the mixing process until the threshold value of the coefficient of variation (CV) or the relative standard deviation (RSD) is reached (the final CV set point value, i.e. fat, fibre, crude protein etc.) and the controller collects the analyzed values and calculate (as the sensor keep updating the values) for the blend uniformity (i.e.

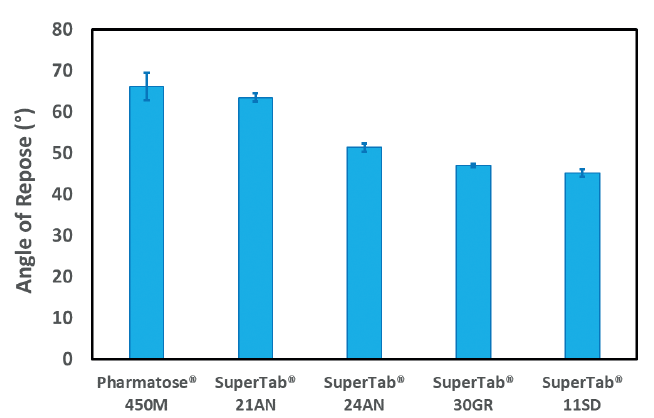
The methods followed the controlled process includes feeding of the individual ingredient hoppers via bucket elevator with their respective ingredients, determining the time of discharge and the rate of discharge that will make for 25 kilogram mass feed per mix, the adoption of virtual multipoint Near Infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) with it accompanying sensor probes that monitors the mixing real time analyzing along as the mixing progresses the various ingredient percentage nutrients classes (i.e. The aim of this research is to develop in a continuous blending system an automated poultry feed mixing process using process controllers. Mixing plays a crucial role in the whole production processes of many industries (ranging from feed mills for poultry birds and other animals, to cement, pharmaceutical, dairy, food etc) in meeting their demand expectations. The study gathers valuable information about the screw feeder performance and input materials properties that can help process understanding and QbD-based development of solid dosages forms in continuous processing lines. A multivariable model involving bulk density (CBD) and parameters from FT4 dynamic downwards testing (SI) and dynamic upwards testing (SE) explained 95.7% of excipients feed rates (p < 0.001). The analysis of the powder conveying by the screws was performed at different hopper fills and different screw speeds. Pharmaceutical excipients with a wide range of material properties were selected and the impact of their flow and density properties on screw feeder performance was investigated. In alignment with Quality by Design (QbD) goals, the aim of this work was to identify and explain critical sources of variability of some powder excipients delivery by screw feeding, in particular to continuous processing lines. Pharmaceutical excipients, such as mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate and anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate can present problems in ensuring a continuous stable feed rate due to their sub-optimal flow properties. Screw feeder performance is a critical aspect in continuous manufacturing processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
